In a significant breakthrough for generative artificial intelligence (AI) in speech, Meta AI researchers have unveiled Voicebox. This groundbreaking model showcases the remarkable ability to generalize to speech-generation tasks beyond its specific training, while maintaining state-of-the-art performance. This blog delves into the details of this extraordinary achievement and explores the diverse capabilities of Voicebox.
A New Approach to Speech Generation
Traditionally, speech synthesizers were limited to training on meticulously prepared data, resulting in monotonous outputs. However, Voicebox builds upon the Flow Matching model—a non-autoregressive generative model developed by Meta. This innovative approach allows Voicebox to learn from unlabeled and diverse speech data, enabling highly non-deterministic mapping between text and speech. With a vast training dataset of over 50,000 hours of recorded speech and transcripts from public domain audiobooks in six languages, Voicebox excels at infilling speech based on contextual information, rendering it incredibly versatile.
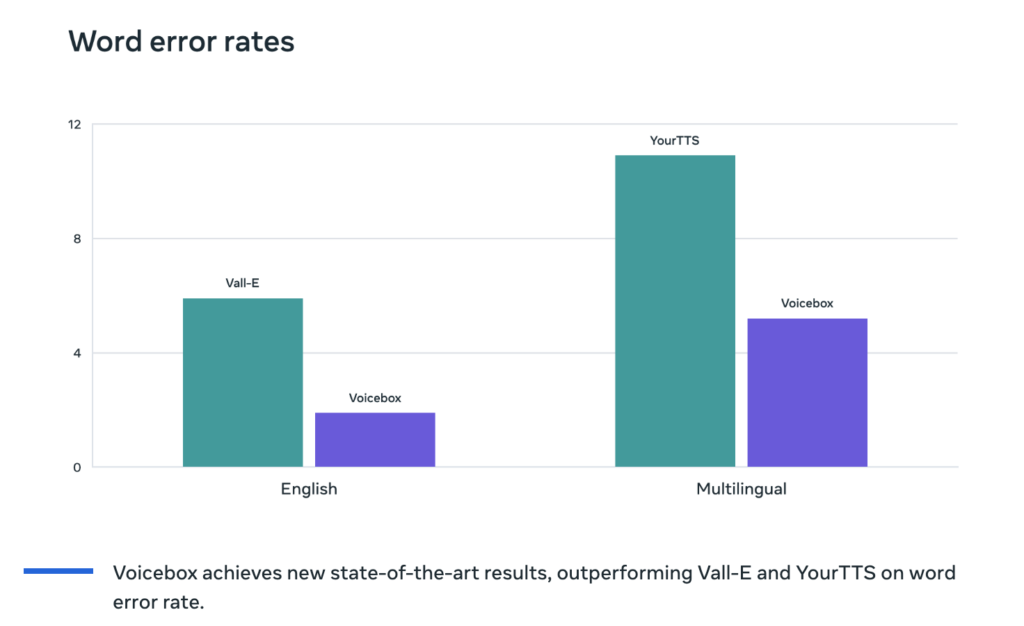
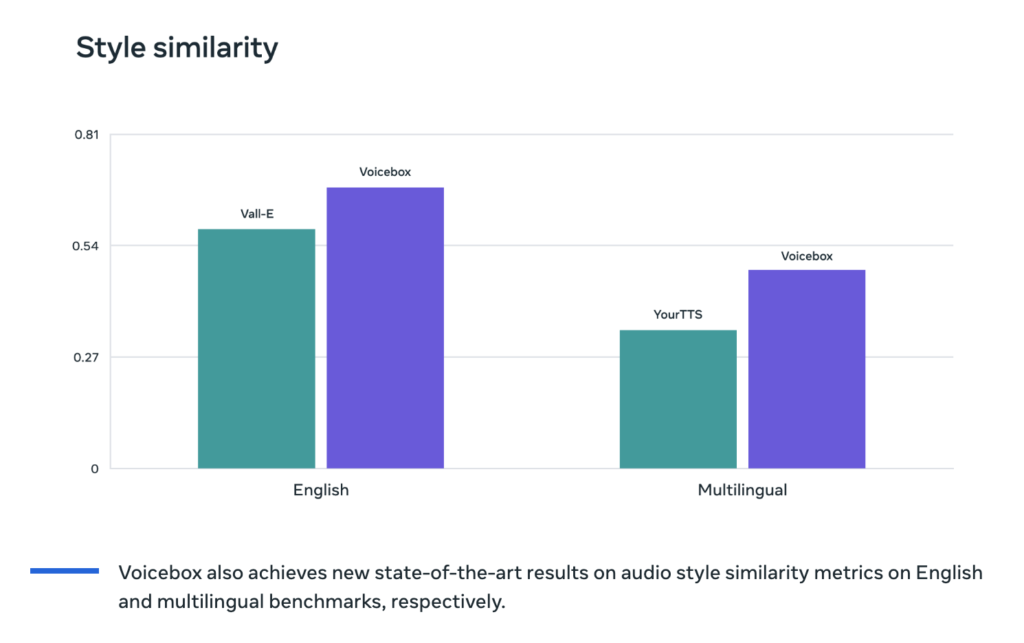
Incredible Capabilities:
In-Context Text-to-Speech Synthesis: Voicebox generates speech in a specific audio style by analyzing a mere two-second input sample. This capability unlocks the potential for projects aimed at assisting individuals who are unable to speak or customizing the voices used by nonplayer characters and virtual assistants.
Cross-Lingual Style Transfer: Utilizing a speech sample and a passage of text, Voicebox can seamlessly produce a reading of the text in English, French, German, Spanish, Polish, or Portuguese. This breakthrough holds tremendous promise for facilitating natural and authentic communication among individuals speaking different languages.
Speech Denoising and Editing: Voicebox seamlessly edits segments within audio recordings by eliminating short-duration noise or replacing misspoken words without the need to re-record the entire speech. This functionality simplifies audio editing and has the potential to make audio cleanup as effortless as popular image-editing tools have made photo adjustments.
Diverse Speech Sampling: Leveraging its learning from diverse real-world data, Voicebox generates speech that faithfully replicates natural conversations. This capability could prove invaluable in generating synthetic data for training speech assistant models. Notably, speech recognition models trained on Voicebox-generated synthetic speech perform nearly as well as models trained on real speech.
Sharing Generative AI Research Responsibly
While Voicebox’s potential is immense, the Meta team recognizes the importance of responsible research and the risks of potential misuse. Consequently, they have opted not to release the Voicebox model or code to the public at this time. However, the team has shared audio samples and a research paper, thoroughly documenting their approach and achievements. Additionally, they have developed a highly effective classifier to distinguish between authentic speech and audio generated by Voicebox, mitigating potential future risks.
Conclusion:
The development of Voicebox signifies a significant milestone in generative AI research for speech. With its remarkable task generalization capabilities, Voicebox has the potential to revolutionize speech generation, akin to the transformative impact of scalable AI models on text, image, and video generation. The Meta team eagerly anticipates the future impact of Voicebox in the audio domain and looks forward to witnessing how other researchers will build upon their work. Through responsible research and knowledge sharing, the AI community can continue pushing the boundaries of technology while addressing the ethical considerations at hand.

